Basic Kidney Information
What do kidneys do and why are they important?
You have two kidneys. Each kidney is about the size of your fist. They are located near the middle of your back, just below the rib cage. Healthy kidneys do many important jobs. For example, kidneys:
- Remove waste products and extra water from your body
- Help control blood pressure
- Help make red blood cells
- Help keep bones healthy
Think of your kidneys as a coffee filter. When you make coffee, the filter keeps the coffee grounds inside, but allows water to pass through. Your kidneys do something similar. They keep the things you need inside your body, but filter out things you don’t need.
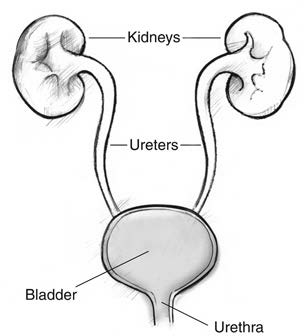
Each of your kidneys has about 1.5 million filters called nephrons. Nephrons remove wastes and extra fluid from your blood in the form of urine. The urine flows through two tubes, called ureters, to the bladder. The urine is stored there until you go to the bathroom. The wastes come from the breakdown of what you eat or drink, medicine you take, plus normal muscle activity.
What is kidney disease?
Chronic kidney disease includes conditions that damage your kidneys and decrease their ability to filter your blood the way they should. This damage can cause wastes to build up in your body.
Who is at risk for kidney disease?
There are a number of environmental and social factors that can increase the likelihood of developing high blood pressure and diabetes, which are the 2 leading risk factors for kidney disease. Your risk is also increased if you are overweight, older than age 60, and have family members with kidney disease.
What causes kidney disease?
Diabetes and high blood pressure are responsible for up to two-thirds of the cases of kidney disease. Other conditions are: glomerulonephritis, diseases that damage the kidney's filtering units, which are the third most common type of kidney disease; inherited diseases, such as polycystic kidney disease; malformations at birth that occur as a baby develops; lupus and other immune diseases; obstructions such as kidney stones or an enlarged prostate; and repeated urinary tract infections.
What are the symptoms of kidney disease?
Most people may not have any severe symptoms until their kidney disease is advanced. However, you may notice that you:
- feel more tired and have less energy
- have trouble concentrating
- have a poor appetite
- have trouble sleeping
- have muscle cramping at night
- have swollen feet and ankles
- have puffiness around your eyes, especially in the morning
- have dry, itchy skin
- need to urinate more often, especially at night.
What happens if kidney disease gets worse? Can kidney disease cause other health problems?
If kidney disease gets worse, wastes can build to high levels in your blood and make you feel sick. You may develop complications like high blood pressure, anemia (low red blood cell count), high potassium (hyperkalemia), weak bones, poor nutrition, and nerve damage. Also, kidney disease increases your risk of having heart and blood vessel disease. These problems may happen slowly over a long period of time.